Array List and Linked List both implements List interface. But which one to use when calls for a discussion. So lets look at the ways in which they differ to decide when to use ArrayList or LinkedList.
Both differ based on following parameters:
Both differ based on following parameters:
1. Insertion or Deletion of element
If there is need for lot of insertion or deletion of a elements in the List, then prefer Linked List as it provides faster insertion or deletion operation in comparison to Array List.
Reason:
Array List requires lots of index shifting to be done for any insertion or deletion operation to be performed as a result performance time increases. Take a glimpse of insertion(13 needs to be inserted at index 2) in diagram given below:
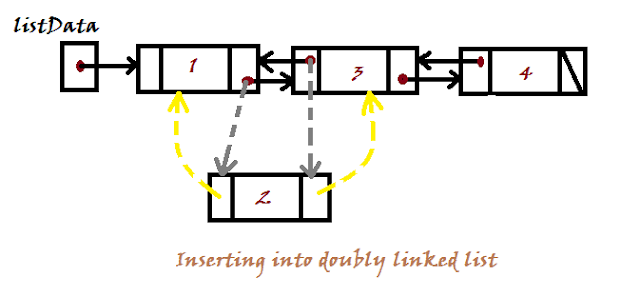
Linked List does not require shifting of many nodes. It just effects three nodes. One which is to be inserted. And the other two are between which it needs to be inserted. Take a glimpse of insertion(node having element 2 needs to be inserted between 1 and 3) in diagram given below.
Linked List does not require shifting of many nodes. It just effects three nodes. One which is to be inserted. And the other two are between which it needs to be inserted. Take a glimpse of insertion(node having element 2 needs to be inserted between 1 and 3) in diagram given below.
Since lots of element don't need to be shifted for performing insertion or deletion operation in case of Linked List (which is in case of Array List), so it performs faster insertion and deletion operation.
2. Searching element from List
If one needs to search or get element from the List then for better performance opt for Array List as it provides faster search operation in comparison to Linked List.
3. Memory consideration
Linked List consumes more memory space in comparison to Array List.
Reason :
Linked List has to maintain extra memory space for storing address data in both forward & backward pointer for each and every node apart from storing the element. Array List does not bother at all about storing any address detail so no extra memory requirement.
4. Storage Mechanism
ArrayList uses dynamic array to store the elements.
LinkedList uses doubly linked list to store the elements.
5. Role
Arraylist can only perform the role of a List as it implements only List interface.
LinkedList can perform the role of both List and Queue as it implements both List and Deque interfaces
Example
Example
package ListExample;
import
java.util.ArrayList;
import
java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
public class ListExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//create ArrayList
List<String>
arrayList = new
ArrayList<String>();
//add element to ArrayList
arrayList.add("Rajneesh");
arrayList.add("Shweta");
arrayList.add("Anup");
//create LinkedList
List<String>
linkedList = new
LinkedList<String>();
//add elements to LinkedList
linkedList.add("Puja");
linkedList.add("Mukesh");
linkedList.add("Titli");
}
}
You may also like to read:
- checked vs unchecked exception
- collection vs collections
- ArrayList vs HashSet
- Iterator vs ListIterator
- ArrayList vs Vector
- Can we overload main() in java?


please provide the reason of why linked list is preferable while insertion/deletion?
ReplyDeleteThanks for pointing that out. We have updated the reason in the post. please, get in touch if still any query persists.
DeleteHi,
ReplyDeleteI have recently faced question that if you have a million records which will not change, what will you use? Arraylist or LinkedList?
Thanks for sharing your question bhavin.
DeleteIf million records are not going to change that means no insertion or removal of elements is involved.In such case we will have operations like getting(fetching) the element from the list. So we can go for arraylist as it offers faster search operation.
For reference you can see point number 2. Searching element from List
crystal clear. Really nice explanation
ReplyDelete